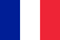
Arthrosis of the knee joint is progressing. As the disease develops, the cartilage first suffers, then the bone elements participate in the destructive process. High physical activity, lack of physical activity, metabolic disorders lead to the causes of the problems.
With the development of the disease, there is a risk of ankylosis, which is accompanied by a decrease in the motor activity of the joint.
Features of the disease

Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is accompanied by deformation and destruction of cartilage. The pathology is characterized by a chronic degenerative nature and causes pain of varying degrees of intensity.
It provokes a complete loss of motor activity and loss of functionality. According to ICD-10, the disease is coded as follows: M17. Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee joint).
Pathologies are more susceptible to women than men. At the same time, the risk of arthrosis is much higher in people with varicose veins and overweight. That is why the disease is more common in obese women over 40. The elderly are also affected. In young people, arthrosis develops as a result of injuries that occurred during physical work or sports activities.
Osteoarthritis must be distinguished from arthritis, which is an inflammatory disease caused by disorders in the immune system. Infectious diseases also lead to the development of arthritis.
In the photo, the clinical picture of arthrosis
stages
Arthrosis of the knee joint has 2 main varieties - primary and secondary. In the first case, the disease appears in childhood and is caused by a violation of the development of the surfaces of the joints or ligaments.
In this situation, the joint faces increased loads, which leads to degenerative changes. The secondary form of arthrosis is associated with injuries and other diseases.
Pathology can be unilateral or bilateral. In the first case, the cause of the disease is most often injuries. The bilateral form of the pathology is usually the result of obesity.
There are several stages of development of arthrosis of the knee joint. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to deal with it.
The main stages of the disease include the following:
- 1 degree- at this stage, people rarely go to the doctor. They feel slight discomfort in the right or left knee, which appears after a long walk. The pain syndrome occurs only after increased physical exertion or strong bending and extension of the knee. When performing radiography, it is possible to see a slight narrowing of the joint gap and the appearance of bone processes in the structure of the joints. The pathology was discovered accidentally during other examinations. At this stage, conservative therapy is sufficient.
- 2 degree- characterized by more obvious symptoms of the disease, which are difficult to ignore. Knee pain is felt constantly. It is especially intense in the morning and evening. Even in a calm state, the discomfort does not disappear. A person's gait slows down, motor activity is impaired, movements in the knee are accompanied by a crunch. There is a risk of complications that are accompanied by a piece of bone or cartilage falling into the joint cavity. This provokes an increase in pain and loss of motor activity. When palpating the knee, there is a risk of severe pain and visible deformation of the joint. Inflammatory processes often develop. In such a situation, the knee swells. When performing X-rays, you can see a strong narrowing of the joint gap, the presence of osteophytes, bone curvature. In such a situation, the patient needs complex treatment. In some cases, it is not possible to do without surgery.
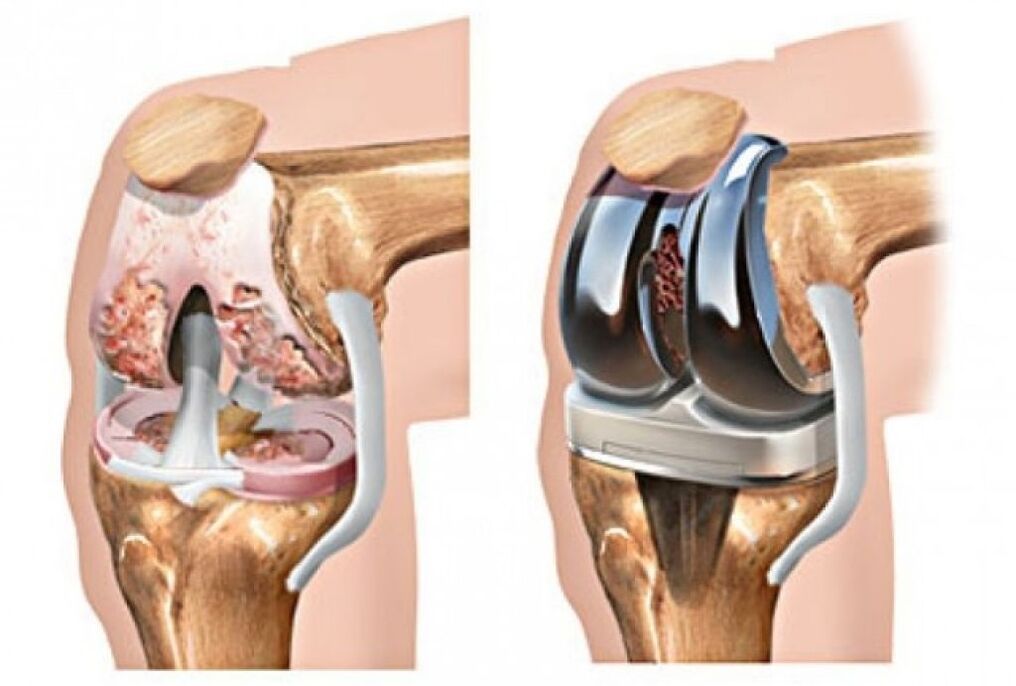
- 3 degree- represents a neglected form of pathology. At this stage, a person receives permanent damage. The patient has constant pain in the knee, impaired motor activity. With every movement, the knee crunches loudly. The joint is characterized by pronounced deformation, increases in size due to fluid accumulation and almost completely loses mobility. When performing radiography, it is possible to see the destruction of the ligament apparatus and menisci, the abrasion of the cartilage and the increase in the size of the connective tissue. Partial fusion of the joints may also be observed. To solve the problem, the affected joint is replaced with an artificial one.
In most cases, patients go to the doctor at the second stage of arthrosis. This is characteristic of the elderly who are accustomed to age-related changes.
Causes of knee osteoarthritis
The main cause of osteoarthritis is an injury to the knee. The damage may be due to exercise, arthritis, or other factors.
The main causes of osteoarthritis of the knee include the following:
- Inflammation of the knee - provoking factors can be arthritis, bursitis and other factors.
- Damage to the meniscus - in the absence of treatment of such a pathology, arthrosis often develops.
- Osteochondropathy of the knee.
- Physical factors - difficult sports, overweight, etc.
- Bone fractures, post-traumatic syndrome.
- Operations for meniscus lesions, arthroscopy, long-term blockades using hormones.
- Pathologies that change the load on the knee. These include flat feet, lesions of the lower back, arthrosis. Hip dysplasia is also included in this category.
Symptoms and signs
The main manifestations of the disease include the following:
- Pain - most often there is mechanical discomfort, which is relieved with painkillers. It can be dull, painful, sharp.
- Crunch while moving.
- Impaired joint mobility.
- Decreased motor activity.
- Weakness of the muscles of the limbs.
- Increase in local temperature in the knee area.
- Gait disorder, which is accompanied by lameness of the legs.
- Violation of stability.
- Knee sprain.
Diagnosis
Before starting the treatment of gonarthrosis, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination.
If you suspect gonarthrosis, you should contact an orthopedic traumatologist. The specialist examines and interviews the patient, assessing the condition of the joint and the range of motion in it.
To identify the pathology, do such tests:
- Magnetic resonance. Using the procedure, it is possible to examine the affected area by obtaining a three-dimensional image. Manipulation shows the vasculature and nerve fibers.
- Radiography. The procedure allows you to identify cracks, dents, bone processes.
What is dangerous arthrosis of the knee
The consequences of arthrosis include inflammation of the joints, atrophic changes in muscle tissues and ligaments, gait disorders. There is also a risk of deformity of the lower limb.
In difficult situations, the disease causes complete degeneration of cartilage and deformation of bone structures. As a result, the mobility of the limb decreases and the person becomes disabled.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the appearance of knee arthrosis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- eat right - the menu should contain a lot of vitamins, minerals, proteins;
- get rid of bad habits;
- weight normalization;
- do sports, walk or ride an ergometer, perform medical complexes;
- avoid injury, protect your legs with knee pads.
The pathology lends itself well to therapy, since the thinning of cartilage tissue is observed only in the third stage. The prognosis is quite favorable.
If therapy is not started in time, there is a risk of damage. Usually the group is defined by the third degree of gonarthrosis. As for military service, they are released from it with the development of a deforming form of the disease.
Knee osteoarthritis is a serious pathology that leads to negative health consequences. To deal with the problem, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner. The specialist will conduct the necessary tests and choose the appropriate therapy.